










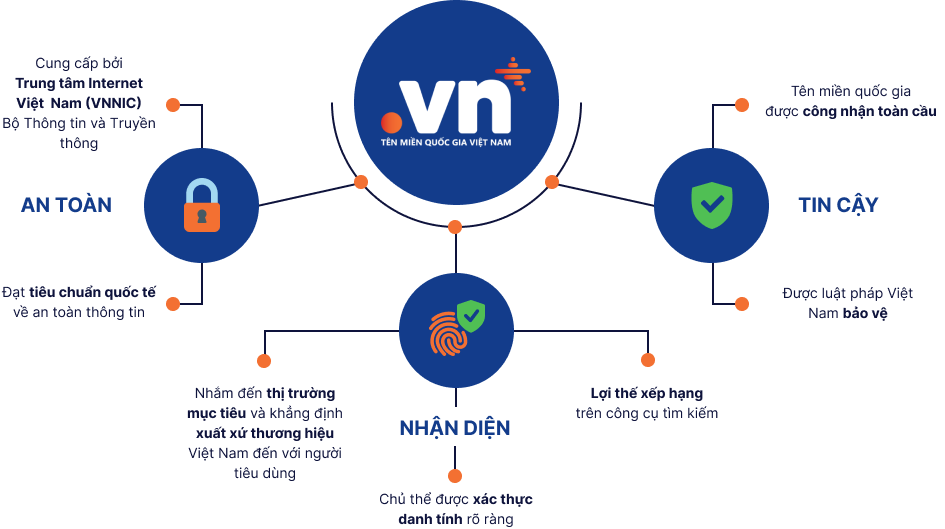


 Chủ
thể
được xác thực danh tính rõ ràng
Chủ
thể
được xác thực danh tính rõ ràng Nhắm
đến thị trường mục tiêu và khẳng định xuất xứ thương hiệu Việt Nam đến với người tiêu
dùng
Nhắm
đến thị trường mục tiêu và khẳng định xuất xứ thương hiệu Việt Nam đến với người tiêu
dùng
 Lợi thế xếp hạng trên công cụ tìm
kiếm
Lợi thế xếp hạng trên công cụ tìm
kiếm

 Cung
cấp bởi Trung tâm Internet Việt Nam (VNNIC) Bộ
Thông tin và Truyền thông
Cung
cấp bởi Trung tâm Internet Việt Nam (VNNIC) Bộ
Thông tin và Truyền thông Đạt
tiêu chuẩn quốc tế về an toàn thông tin
Đạt
tiêu chuẩn quốc tế về an toàn thông tin


 Tên
miền quốc gia được công nhận toàn cầu
Tên
miền quốc gia được công nhận toàn cầu  Được
luật pháp Việt Nam bảo vệ
Được
luật pháp Việt Nam bảo vệ 
Cindy Lê
Founder, Devons Vietnam
“Thương hiệu thời trang của tôi được biết đến ở nhiều nước trên thế giới, tôi sử dụng tên miền .vn như một lời khẳng định về xuất xứ thương hiệu, và luôn tự hào là một thương hiệu Việt Nam”
Đăng Huy
tuoithobencon.vn
“Chúng tôi tin tưởng lựa chọn tên miền ".vn" bởi ".vn" là thương hiệu của quốc gia, và định vị trực tiếp đến khách hàng Việt. Do đó, chúng tôi đã chọn làm trang bán hàng online với tên miền ".vn" mà không phải là các đuôi tên miền khác.”
Thanh Mai
Founder, High Tea Story Vietnam
“Là một thương hiệu phân phối trà Anh Quốc tại Việt Nam, lựa chọn đầu tiên của tôi là tên miền highteastory.vn cho thương hiệu của mình. Theo tôi, tên miền này giúp tôi hướng đến thị trường trong nước hiệu quả hơn!”
Cindy Lê
Founder, Devons Vietnam
“Thương hiệu thời trang của tôi được biết đến ở nhiều nước trên thế giới, tôi sử dụng tên miền .vn như một lời khẳng định về xuất xứ thương hiệu, và luôn tự hào là một thương hiệu Việt Nam”
Đăng Huy
tuoithobencon.vn
“Chúng tôi tin tưởng lựa chọn tên miền ".vn" bởi ".vn" là thương hiệu của quốc gia, và định vị trực tiếp đến khách hàng Việt. Do đó, chúng tôi đã chọn làm trang bán hàng online với tên miền ".vn" mà không phải là các đuôi tên miền khác.”
Thanh Mai
Founder, High Tea Story Vietnam
“Là một thương hiệu phân phối trà Anh Quốc tại Việt Nam, lựa chọn đầu tiên của tôi là tên miền highteastory.vn cho thương hiệu của mình. Theo tôi, tên miền này giúp tôi hướng đến thị trường trong nước hiệu quả hơn!”
Cindy Lê
Founder, Devons Vietnam
“Thương hiệu thời trang của tôi được biết đến ở nhiều nước trên thế giới, tôi sử dụng tên miền .vn như một lời khẳng định về xuất xứ thương hiệu, và luôn tự hào là một thương hiệu Việt Nam”


